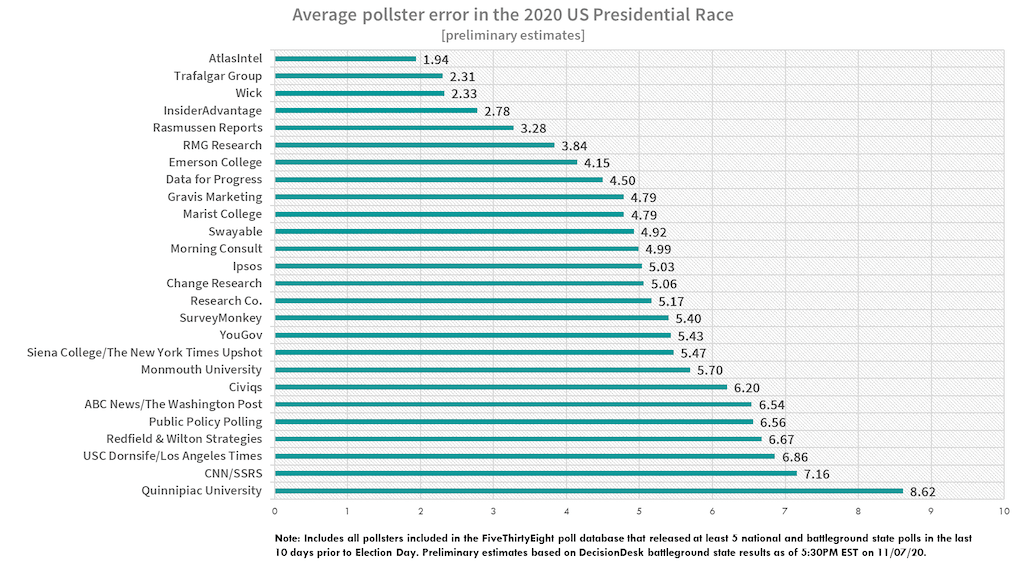
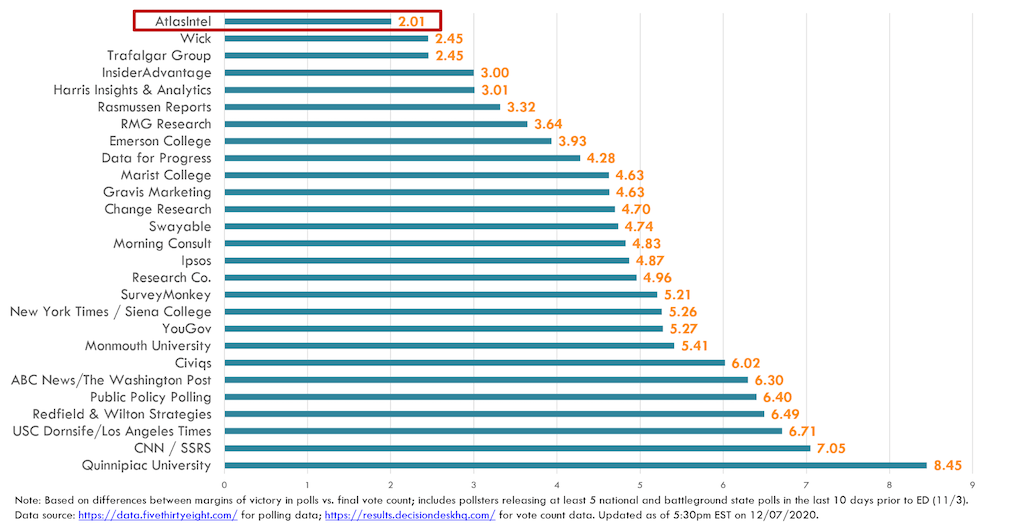
Atlas Intel polling bias has become a significant topic of discussion in recent years, particularly in the context of political and social surveys. Understanding what polling bias is, how it affects data interpretation, and its implications is crucial for anyone interested in data-driven decision-making. This article aims to provide a detailed exploration of this subject, covering everything from the basics to advanced concepts.
Polling bias is not a new phenomenon, but advancements in technology and data collection methods have brought it to the forefront of public discourse. As organizations like Atlas Intel continue to conduct surveys and analyze data, it's essential to understand how bias can creep into these processes and affect outcomes.
In this article, we will delve into the intricacies of polling bias, explore its causes, effects, and potential solutions. By the end, you'll have a thorough understanding of how polling bias works and why it matters in today's data-driven world.
Read also:Katy Robertson A Comprehensive Exploration Of Her Career And Impact In The Adult Entertainment Industry
Table of Contents
- What is Atlas Intel Polling Bias?
- Types of Polling Bias
- Causes of Polling Bias
- Effects on Data Interpretation
- Case Studies: Real-World Examples
- How to Reduce Polling Bias
- The Role of Technology in Mitigating Bias
- Ethical Considerations
- Importance of Transparency
- The Future of Polling
What is Atlas Intel Polling Bias?
Polling bias refers to systematic errors or distortions that occur during the process of collecting and analyzing survey data. In the context of Atlas Intel, these biases can significantly impact the accuracy and reliability of polling results. Polling bias arises when certain groups are overrepresented or underrepresented in a survey sample, leading to skewed results.
Definition and Overview
Polling bias is not always intentional; it can result from various factors such as sampling errors, question phrasing, or respondent behavior. For organizations like Atlas Intel, ensuring unbiased polling is critical for maintaining credibility and providing accurate insights to stakeholders.
Why Does It Matter?
In today's world, where data drives decision-making in politics, marketing, and public policy, polling bias can have far-reaching consequences. Misleading data can lead to incorrect conclusions, affecting everything from election outcomes to business strategies.
Types of Polling Bias
Polling bias can manifest in several forms, each with its own set of implications. Understanding these types is essential for identifying and addressing them effectively.
Read also:Humanjaylen Leaks A Comprehensive Exploration And Analysis
- Sampling Bias: Occurs when the sample does not accurately represent the population being surveyed.
- Nonresponse Bias: Happens when certain groups are less likely to respond to surveys, leading to an unbalanced sample.
- Questionnaire Bias: Arises from poorly worded or leading questions that influence respondents' answers.
- Selection Bias: Results from the method used to select participants, which may favor certain groups over others.
Causes of Polling Bias
Several factors contribute to polling bias, and addressing them requires a multifaceted approach. Below are some of the primary causes:
1. Inadequate Sampling Techniques
Using outdated or insufficient sampling methods can lead to underrepresentation of certain demographics, resulting in biased data.
2. Poor Question Design
Questions that are ambiguous, leading, or overly complex can influence respondents' answers, introducing bias into the results.
3. Technological Limitations
Reliance on certain technologies, such as online surveys, may exclude populations without internet access, creating a skewed sample.
Effects on Data Interpretation
Polling bias can have severe consequences on how data is interpreted and used. Misleading results can lead to incorrect conclusions, affecting decision-making processes across various sectors.
1. Political Implications
Inaccurate polling data can influence public perception and voter behavior, potentially altering election outcomes.
2. Business Decisions
Companies relying on biased survey data may make ill-informed decisions, leading to financial losses or missed opportunities.
3. Public Policy
Governments using flawed polling data to shape policies may inadvertently harm certain populations or fail to address critical issues effectively.
Case Studies: Real-World Examples
Examining real-world examples of polling bias can provide valuable insights into its effects and potential solutions.
1. The 2016 U.S. Presidential Election
Many pre-election polls underestimated support for Donald Trump, highlighting the challenges of accurately predicting voter behavior.
2. Brexit Referendum
Polling data suggested a close race, but the actual outcome surprised many, emphasizing the importance of addressing bias in polling methods.
How to Reduce Polling Bias
Mitigating polling bias requires a combination of methodological improvements and technological advancements. Here are some strategies:
- Use Random Sampling: Ensure that samples are randomly selected to represent the entire population.
- Refine Question Design: Develop clear, neutral questions that minimize respondent influence.
- Employ Multiple Channels: Utilize a variety of survey methods to reach diverse populations.
- Implement Weighting Techniques: Adjust results to account for overrepresentation or underrepresentation of certain groups.
The Role of Technology in Mitigating Bias
Technology plays a crucial role in reducing polling bias by enabling more accurate data collection and analysis.
1. Advanced Analytics
Machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and anomalies in survey data, helping to detect and correct bias.
2. Mobile Surveys
Mobile technology expands survey reach, allowing organizations to gather data from previously underserved populations.
Ethical Considerations
Addressing polling bias also involves ethical considerations, particularly in ensuring fairness and accuracy in data representation.
1. Transparency
Organizations must be transparent about their methodologies and potential limitations to maintain trust with stakeholders.
2. Inclusivity
Polling efforts should strive to include all demographic groups, avoiding marginalization of any population.
Importance of Transparency
Transparency is vital in building trust with the public and stakeholders. Organizations like Atlas Intel must disclose their methodologies, data sources, and potential biases to ensure credibility.
The Future of Polling
As technology continues to evolve, the future of polling looks promising. Advances in artificial intelligence, data analytics, and mobile technology will likely lead to more accurate and inclusive surveys, reducing the impact of polling bias.
Conclusion
Atlas Intel polling bias is a complex issue with significant implications for data-driven decision-making. By understanding its causes, effects, and potential solutions, we can work towards more accurate and reliable polling methods. We encourage readers to engage with this topic by leaving comments, sharing this article, and exploring related content on our site.
Together, we can promote transparency, inclusivity, and accuracy in polling practices, ensuring that data serves as a reliable tool for shaping our world.
References:
- Smith, J. (2020). "The Impact of Polling Bias on Election Outcomes." Journal of Political Science.
- Johnson, R. (2021). "Technological Innovations in Survey Methodology." Data Analytics Quarterly.
- Williams, L. (2019). "Ethical Considerations in Polling Practices." Ethics in Research.