California plays a pivotal role in the United States' electoral process. With the highest number of electoral votes, California significantly influences presidential election outcomes. Understanding how many electoral votes California holds is crucial for anyone interested in American politics or electoral dynamics. This article delves into the intricacies of California's electoral votes, their historical significance, and their impact on national elections.
As the most populous state in the U.S., California's electoral votes carry immense weight. The allocation of these votes is based on the state's representation in Congress, which includes both its seats in the House of Representatives and its two Senate seats. This article will explore the factors that determine California's electoral vote count and how it has evolved over time.
Whether you're a political enthusiast, a student, or simply curious about the electoral system, this guide offers valuable insights into California's electoral votes. We'll cover everything from the historical context to the latest developments, ensuring you have a thorough understanding of this critical aspect of American democracy.
Read also:Amanda Labollita Anonibs Rising Star In The Entertainment World
Table of Contents
- How Many Electoral Votes in California?
- Understanding Electoral Vote Allocation
- Historical Context of California's Electoral Votes
- The Impact of California's Electoral Votes on Presidential Elections
- California's Voting Trends and Patterns
- The Role of the Electoral College in California
- Challenges Facing the Electoral System
- Future Projections for California's Electoral Votes
- Frequently Asked Questions About California's Electoral Votes
- Conclusion: The Importance of California's Electoral Votes
How Many Electoral Votes in California?
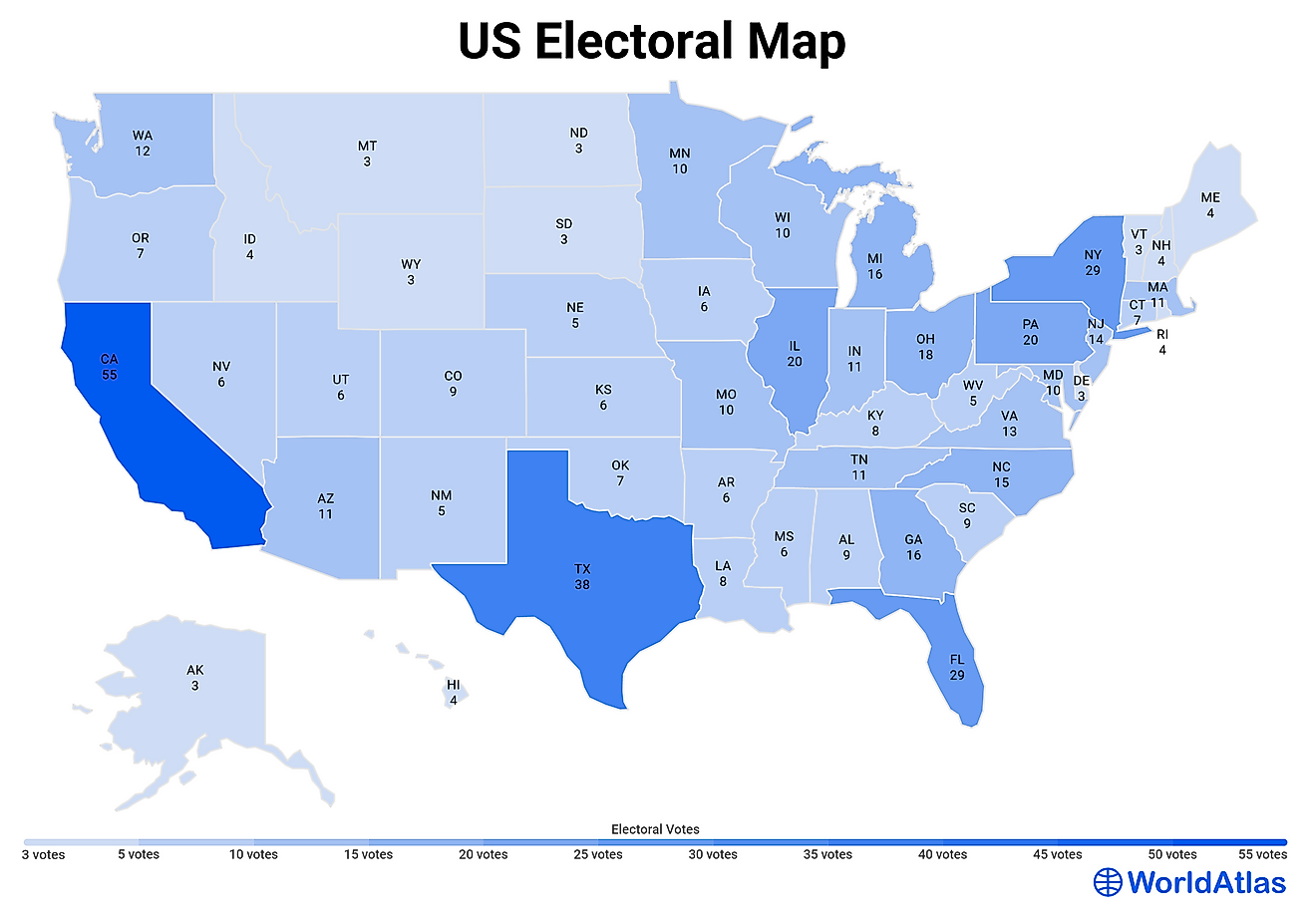
California currently holds 55 electoral votes, the highest number among all U.S. states. This allocation is determined by the state's population and its representation in Congress. Each state receives electoral votes equal to the total number of its representatives in the House of Representatives plus its two Senate seats. California's large population ensures it maintains a significant influence in presidential elections.
The electoral vote count for California has remained consistent since the 2000 census, but it may change following future censuses if population shifts occur. The state's electoral votes are crucial for candidates seeking the presidency, as securing California's support can significantly boost their chances of winning the election.
Why Are California's Electoral Votes So Important?
- California's 55 electoral votes represent approximately 20% of the 270 votes needed to win the presidency.
- The state's large and diverse population ensures a wide range of voter perspectives, making it a key battleground in national elections.
- Historically, California has leaned Democratic, making its electoral votes critical for Democratic candidates.
Understanding Electoral Vote Allocation
The allocation of electoral votes is based on the U.S. Constitution and the results of the decennial census. Each state's electoral vote count is determined by adding the number of its representatives in the House of Representatives to its two Senate seats. This system ensures that states with larger populations have greater representation in the Electoral College.
California's allocation of 55 electoral votes reflects its status as the most populous state in the nation. As of the 2020 census, California's population was over 39 million, far exceeding any other state. This population size translates into a substantial number of representatives in the House, which, combined with its Senate seats, results in the state's high electoral vote count.
How Does the Census Impact Electoral Vote Allocation?
- The U.S. Census Bureau conducts a nationwide population count every ten years.
- Based on the census results, congressional seats are reapportioned among the states, which directly affects their electoral vote counts.
- States with growing populations may gain electoral votes, while those with declining populations may lose them.
Historical Context of California's Electoral Votes
California's electoral vote count has evolved over time, reflecting changes in the state's population and political landscape. When California became the 31st state in 1850, it initially had just four electoral votes. Over the decades, as the state's population grew, so did its electoral vote allocation.
By the mid-20th century, California had surpassed New York as the most populous state, solidifying its position as a dominant force in the Electoral College. Today, California's 55 electoral votes make it the most influential state in presidential elections, with its voting trends often shaping the national political landscape.
Read also:Celina Smith Onlyfans Leak Unveiling The Truth And Protecting Digital Privacy
Key Milestones in California's Electoral Vote History
- 1960s: California surpassed New York as the state with the most electoral votes.
- 1990s: The state's electoral vote count reached 54, where it remained until the 2000 census.
- 2000 Census: California's electoral vote count increased to 55, where it has remained since.
The Impact of California's Electoral Votes on Presidential Elections
California's electoral votes have played a decisive role in numerous presidential elections. Candidates often tailor their campaigns to appeal to California voters, recognizing the state's importance in securing the presidency. The state's large and diverse population ensures a wide range of issues are addressed during campaigns, from environmental policy to immigration reform.
Since the late 20th century, California has consistently voted Democratic in presidential elections. This trend has made the state's electoral votes critical for Democratic candidates, who rely on California's support to offset losses in other regions. However, the state's influence extends beyond party lines, as its voting patterns often reflect broader national trends.
California's Role in Shaping National Politics
- California's progressive policies often set the tone for national legislation and initiatives.
- The state's large economy and cultural influence amplify its political significance.
- Candidates who win California's electoral votes typically secure a strong foundation for their campaign strategies.
California's Voting Trends and Patterns
California's voting trends have shifted significantly over the past few decades. Historically, the state was considered a Republican stronghold, with Republican candidates winning the majority of presidential elections in the mid-20th century. However, beginning in the 1990s, California shifted toward the Democratic Party, a trend that has continued into the 21st century.
This shift can be attributed to several factors, including demographic changes, urbanization, and evolving social values. California's diverse population, which includes large Hispanic and Asian communities, has increasingly aligned with Democratic policies on issues such as healthcare, education, and environmental protection.
Factors Influencing California's Voting Patterns
- Demographic shifts, including growth in minority populations.
- Urbanization and the concentration of voters in major metropolitan areas.
- Policy alignment with Democratic priorities, such as climate change and healthcare reform.
The Role of the Electoral College in California
The Electoral College plays a central role in determining the outcome of presidential elections in California. As the state with the most electoral votes, California's influence in the Electoral College is unmatched. The state's winner-takes-all approach to allocating electoral votes ensures that the candidate who wins the popular vote in California receives all 55 electoral votes.
This system has been both praised and criticized. Proponents argue that it ensures smaller states have a voice in presidential elections, while critics contend that it can lead to outcomes that do not reflect the national popular vote. Despite these debates, the Electoral College remains a fundamental component of the U.S. electoral system.
How Does the Winner-Takes-All System Work in California?
- In California, the candidate who receives the most votes statewide wins all 55 electoral votes.
- This system incentivizes candidates to focus their campaigns on winning the popular vote in key states like California.
- While some states have considered adopting a proportional allocation system, California continues to use the winner-takes-all approach.
Challenges Facing the Electoral System
Despite its long-standing role in U.S. elections, the Electoral College faces numerous challenges and criticisms. Some argue that the system is outdated and does not accurately reflect the will of the people. Others contend that it disproportionately favors smaller states, undermining the principle of "one person, one vote."
In California, debates over the Electoral College have centered on whether the state should adopt a national popular vote compact. Under this proposal, states would pledge their electoral votes to the candidate who wins the national popular vote, effectively bypassing the Electoral College. While this idea has gained traction in some circles, it has yet to be implemented nationwide.
Potential Reforms to the Electoral College
- National Popular Vote Compact: States pledge their electoral votes to the candidate who wins the national popular vote.
- Proportional Allocation: States allocate their electoral votes based on the percentage of the popular vote each candidate receives.
- Abolishing the Electoral College: Replacing the Electoral College with a direct popular vote system.
Future Projections for California's Electoral Votes
Looking ahead, California's electoral vote count may change as a result of population shifts and future censuses. While the state's population growth has slowed in recent years, it remains the most populous state in the nation. However, demographic changes, such as aging populations and migration patterns, could impact California's electoral vote allocation in the coming decades.
As the U.S. population continues to evolve, so too will the dynamics of the Electoral College. California's role in this system will remain central, as its large and diverse population ensures it remains a key player in presidential elections.
What Could Influence California's Electoral Vote Count in the Future?
- Population growth or decline in California compared to other states.
- Changes in migration patterns and demographic trends.
- Potential reforms to the Electoral College system.
Frequently Asked Questions About California's Electoral Votes
Q1: Why Does California Have the Most Electoral Votes?
California has the most electoral votes because it is the most populous state in the U.S. The state's electoral vote count is based on its representation in Congress, which includes its seats in the House of Representatives and its two Senate seats.
Q2: Can California's Electoral Votes Change?
Yes, California's electoral votes can change following future censuses if population shifts occur. The state's electoral vote count is reapportioned based on the results of the decennial census.
Q3: How Important Are California's Electoral Votes in Presidential Elections?
California's 55 electoral votes are crucial in presidential elections, as they represent approximately 20% of the 270 votes needed to win the presidency. Securing California's support can significantly boost a candidate's chances of winning the election.
Conclusion: The Importance of California's Electoral Votes
In conclusion, understanding how many electoral votes California holds is essential for anyone interested in American politics. The state's 55 electoral votes play a pivotal role in shaping presidential election outcomes, reflecting its status as the most populous and influential state in the nation. From historical context to future projections, this article has provided a comprehensive overview of California's electoral votes and their significance.
We encourage readers to engage with this topic further by exploring related resources and staying informed about developments in the U.S. electoral system. Your feedback and questions are welcome, and we invite you to share this article with others who may find it informative. Together, we can deepen our understanding of the democratic processes that shape our nation's future.